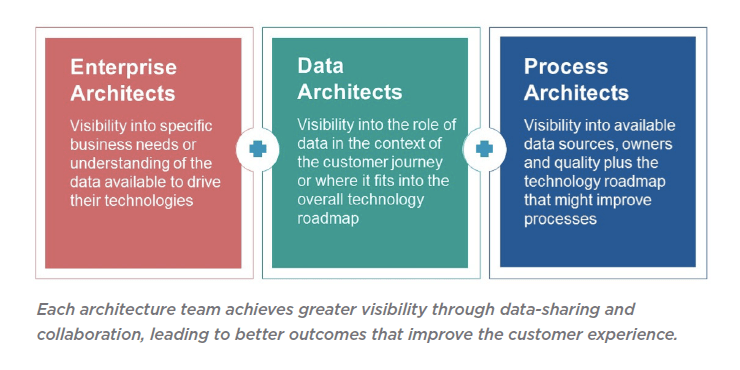
In the current data-driven business climate, the benefits of process and process-based strategy are more desirable to organizations than ever.
Industry regulations and competition traditionally have driven organizational change, but such “transformation” has rarely been comprehensive or truly transformative. Rather, organizational transformation has come in waves, forcing companies and their IT ecosystems to ride them as best as they can – sometimes their fortunes have risen, and sometimes they have waned.
The advent of Brexit and GDPR have again forced today’s organizations to confront external stimuli’s impact on their operations. The difference is that the modern, process-based enterprises can better anticipate these sorts of mandates, incorporate them into their strategic plans, and even leapfrog ahead of their requirements by initiating true internal transformation initiatives – ones based on effectively managed and well-documented business processes.
Shifting Attitudes
Traditional organizations focus almost exclusively on rigid structures, centralized management and accountability; concentrated knowledge; service mainly to external customers; and reactive, short-term strategy alignment driven mainly by massive-scale projects. This traditional approach results in large, unwieldy and primarily reactive organizations that rely either on legacy strengths or inertia for survival.
But as technology evolves and proliferates, more and more organizations are realizing they need to adjust their traditional thinking and subsequent actions, even if just slightly, to gain strategic advantage, reduce costs and retain market dominance. For example:
- Structures are becoming more adaptable, allowing for greater flexibility and cost management. How is this possible and why now? Organizations are grasping that effective, well-managed and documented business processes should form their operational backbones.
- Business units and the departments within them are becoming accountable not only for their own budgets but also on how well they achieve their goals. This is possible because their responsibilities and processes can be clearly defined, documented and then monitored to ensure their work is executed in a repeatable, predictable and measurable way.
- Knowledge is now both centralized and distributed thanks to modern knowledge management systems. Central repositories and collaborative portals give everyone within the organization equal access to the data they need to do their jobs more effectively and efficiently.
- And thanks to all the above, organizations can expand their focus from external customers to internal ones as well. By clearly identifying individual processes (and their cross-business handover points) and customer touchpoints, organizations can interact with any customer at the right point with the most appropriate resources.
If business drivers are connected to processes with appropriate accountability, they become measurable in dimensions never before possible. Such elements as customer-journey quality and cost, process-delivery efficiency and even bottom-up cost aggregation can be captured. Strategic decision-making then becomes infinitely practical and forward-looking.
With this interconnected process – and information – based ecosystem, management can perform accurate and far-reaching impact analyses, test alternate scenarios, and evaluate their costs and implementation possibilities (and difficulties) to make decisions with full knowledge of their implications. Organizational departments can provide real-time feedback on designs and projects, turning theoretical designs into practical plans with buy-in at the right levels.
Benefits of Process
As stated above, one of the key benefits of process and a process-based organizational engine is that organizations should be able to better handle outside pressures, such as new regulations, if they are – or are becoming – truly process-based. Because once processes (and their encompassing business architecture) become central to the organization, a wide array of things become simpler, faster and cheaper.
The benefits of process don’t stop there either. Application design – the holy grail or black hole of budgetary spending and project management, depending on your point of view – is streamlined, with requirements clearly gathered and managed in perfect correspondence to the processes they serve and with the data they manage clearly documented and communicated to the developers. Testing occurs against real-life scenarios by the responsible parties as documented by the process owners – a drastic departure from the more traditional approaches in which the responsibility fell to designated, usually technical application owners.
Finally – and most important – data governance is no longer the isolated domain of data architects but central to the everyday processes that make an organization tick. As processes have stakeholders who use information – data – the roles of technical owners and data stewards become integral to ensuring processes operate efficiently, effectively and – above all – without interruptions. On the other side of this coin, data owners and data stewards no longer operate in their own worlds, distant from the processes their data supports.
Seizing a Process-Based Future
Process is a key axis along which the modern organization must operate. Data governance is another, with cost management becoming a third driver for the enterprise machine. But as we all know, it takes more than stable connecting rods to make an engine work – it needs cogs and wheels, belts and multiple power sources, all working together.
In the traditional organization, people are the internal mechanics. But one can’t escape visions of Charlie Chaplin’s Modern Times worker hopelessly entangled in the machine on which he was working. That’s why, these days, powerful and flexible workflow engines provide much-needed automation for greater visibility plus more power, stability and quality – all the things a machine needs to operate as required/designed.
Advanced process management systems are becoming essential, not optional. And while not as sexy or attention-grabbing as other technologies, they provide the power to drive an organization toward its goals quickly, cost-effectively and efficiently.
To learn how erwin can empower a modern, process-based organization, please click here.