The need for an effective data modeling tool is more significant than ever.
For decades, data modeling has provided the optimal way to design and deploy new relational databases with high-quality data sources and support application development. But it provides even greater value for modern enterprises where critical data exists in both structured and unstructured formats and lives both on premise and in the cloud.
In today’s hyper-competitive, data-driven business landscape, organizations are awash with data and the applications, databases and schema required to manage it.
For example, an organization may have 300 applications, with 50 different databases and a different schema for each. Additional challenges, such as increasing regulatory pressures – from the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) to the Health Insurance Privacy and Portability Act (HIPPA) – and growing stores of unstructured data also underscore the increasing importance of a data modeling tool.
Data modeling, quite simply, describes the process of discovering, analyzing, representing and communicating data requirements in a precise form called the data model. There’s an expression: measure twice, cut once. Data modeling is the upfront “measuring tool” that helps organizations reduce time and avoid guesswork in a low-cost environment.
From a business-outcome perspective, a data modeling tool is used to help organizations:
- Effectively manage and govern massive volumes of data
- Consolidate and build applications with hybrid architectures, including traditional, Big Data, cloud and on premise
- Support expanding regulatory requirements, such as GDPR and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
- Simplify collaboration across key roles and improve information alignment
- Improve business processes for operational efficiency and compliance
- Empower employees with self-service access for enterprise data capability, fluency and accountability
Evaluating a Data Modeling Tool – Key Features
Organizations seeking to invest in a new data modeling tool should consider these four key features.
- Ability to visualize business and technical database structures through an integrated, graphical model.
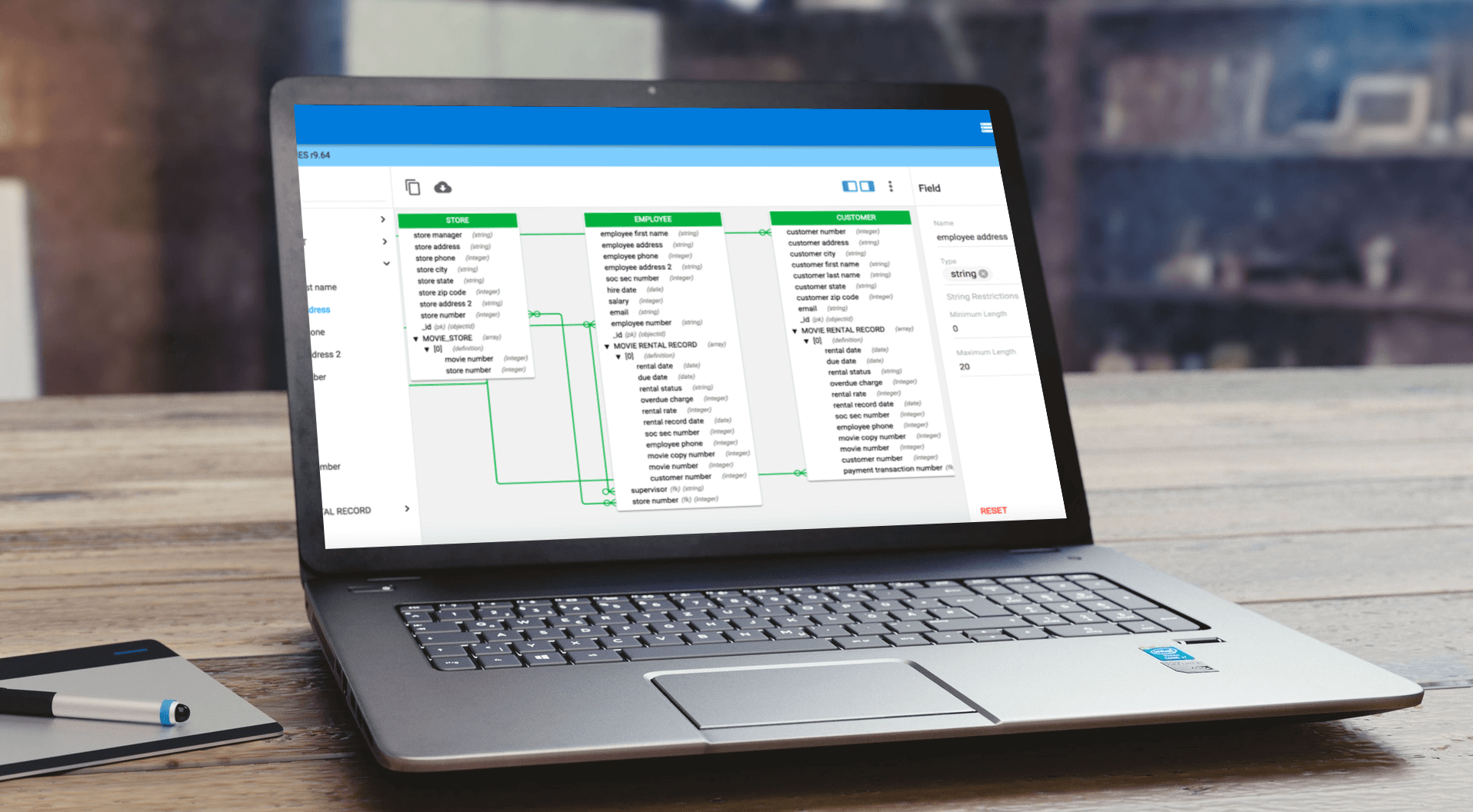
Due to the amount of database platforms available, it’s important that an organization’s data modeling tool supports a sufficient (to your organization) array of platforms. The chosen data modeling tool should be able to read the technical formats of each of these platforms and translate them into highly graphical models rich in metadata. Schema can be deployed from models in an automated fashion and iteratively updated so that new development can take place via model-driven design.
- Empowering of end-user BI/analytics by data source discovery, analysis and integration.
A data modeling tool should give business users confidence in the information they use to make decisions. Such confidence comes from the ability to provide a common, contextual, easily accessible source of data element definitions to ensure they are able to draw upon the correct data; understand what it represents, including where it comes from; and know how it’s connected to other entities.
A data modeling tool can also be used to pull in data sources via self-service BI and analytics dashboards. The data modeling tool should also have the ability to integrate its models into whatever format is required for downstream consumption.
- The ability to store business definitions and data-centric business rules in the model along with technical database schemas, procedures and other information.
With business definitions and rules on board, technical implementations can be better aligned with the needs of the organization. Using an advanced design layer architecture, model “layers” can be created with one or more models focused on the business requirements that then can be linked to one or more database implementations. Design-layer metadata can also be connected from conceptual through logical to physical data models.
- Rationalize platform inconsistencies and deliver a single source of truth for all enterprise business data.
Many organizations struggle to breakdown data silos and unify data into a single source of truth, due in large part to varying data sources and difficulty managing unstructured data. Being able to model any data from anywhere accounts for this with on-demand modeling for non-relational databases that offer speed, horizontal scalability and other real-time application advantages.
With NoSQL support, model structures from non-relational databases, such as Couchbase and MongoDB can be created automatically. Existing Couchbase and MongoDB data sources can be easily discovered, understood and documented through modeling and visualization. Existing entity-relationship diagrams and SQL databases can be migrated to Couchbase and MongoDB too. Relational schema also will be transformed to query-optimized NoSQL constructs.
Other considerations include the ability to:
- Compare models and databases.
- Increase enterprise collaboration.
- Perform impact analysis.
- Enable business and IT infrastructure interoperability.
When it comes to data modeling, no one knows it better. For more than 30 years, erwin Data Modeler has been the market leader. It is built on the vision and experience of data modelers worldwide and is the de-facto standard in data model integration.
You can learn more about driving business value and underpinning governance with erwin DM in this free white paper.