In the first two posts of this series, we focused on the “volume” and “velocity” of Big Data, respectively. In this post, we’ll cover “variety,” the third of Big Data’s “three Vs.” In particular, I plan to discuss NoSQL and NewSQL databases and their implications for data modeling.
As the volume and velocity of data available to organizations continues to rapidly increase, developers have chafed under the performance shackles of traditional relational databases and SQL.
An astonishing array of database solutions have arisen during the past decade to provide developers with higher performance solutions for various aspects of managing their application data. These have been collectively labeled as NoSQL databases.
Originally NoSQL meant that “no SQL” was required to interface with the database. In many cases, developers viewed this as a positive characteristic.
However, SQL is very useful for some tasks, with many organizations having rich SQL skillsets. Consequently, as more organizations demanded SQL as an option to complement some of the new NoSQL databases, the term NoSQL evolved to mean “not only SQL.” This way, SQL capabilities can be leveraged alongside other non-traditional characteristics.
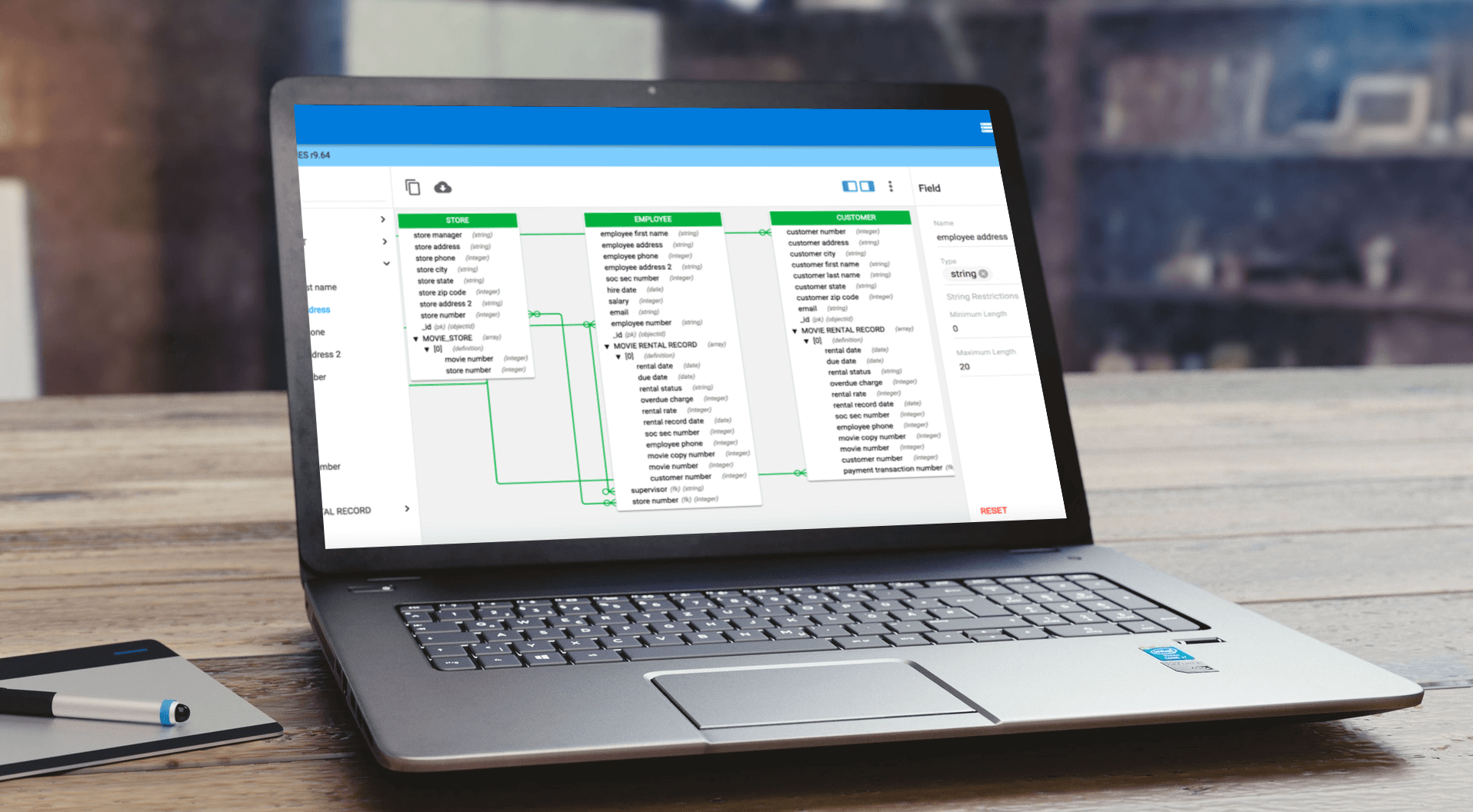
Among the most popular of these new NoSQL options are document databases like MongoDB. MongoDB offers the flexibility to vary fields from document to document and change structure over time. Document databases typically store data in JSON-like documents, making it easy to map to objects in application code.
As the scale of NoSQL deployments in some organizations has rapidly grown, it has become increasingly important to have access to enterprise-grade tools to support modeling and management of NoSQL databases and to incorporate such databases into the broader enterprise data modeling and governance fold.
While document databases, key-value databases, graph databases and other types of NoSQL databases have added valuable options for developers to address various challenges posed by the “three Vs,” they did so largely by compromising consistency in favor of availability and speed, instead offering “eventual consistency.” Consequently, most NoSQL stores lack true ACID transactions, though there are exceptions, such as Aerospike and MarkLogic.
But some organizations are unwilling or unable to forgo consistency and transactional requirements, giving rise to a new class of modern relational database management systems (RDBMS) that aim to guarantee ACIDity while also providing the same level of scalability and performance offered by NoSQL databases.
NewSQL databases are typically designed to operate using a shared nothing architecture. VoltDB is one prominent example of this emerging class of ACID-compliant NewSQL RDBMS. The logical design for NewSQL database schemas is similar to traditional RDBMS schema design, and thus, they are well supported by popular enterprise-grade data modeling tools such as erwin DM.
Whatever mixture of databases your organization chooses to deploy for your OLTP requirements on premise and in the cloud – RDBMS, NoSQL and/or NewSQL – it’s as important as ever for data-driven organizations to be able to model their data and incorporate it into an overall architecture.
When it comes to organizations’ analytics requirements, including data that may be sourced from a wide range of NoSQL, NewSQL RDBMS and unstructured sources, leading organizations are adopting a variety of approaches, including a hybrid approach that many refer to as Managed Data Lakes.
Please join us next time for the fourth installment in our series: Data Modeling in a Jargon-filled World – Managed Data Lakes.