Neo4j enables you to add properties to relationships to describe connections between nodes in physical models. However, in logical models, relationship properties are not supported directly.
Using Edge Mapping, you can add mediator entities in logical models to store relationship properties that are available in relationships in corresponding physical models. This conversion simplifies:
-
Mapping relationship properties in logical models
-
Converting logical relationships to physical edges
-
Maintaining relationship properties consistently across physical and logical models
Mapping Relationship Properties from Physical Edges into Logical Models
You can map relationship properties into the logical model by converting a physical relationship into an edge, which creates a mediator entity to store those properties.
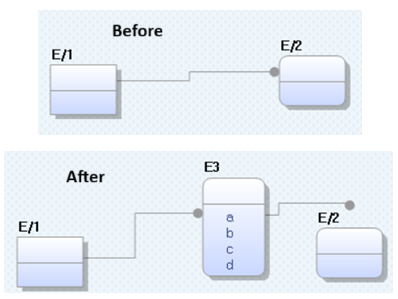
For example, the following image shows a physical model with a relationship between entities E_1 and E_2.

You can convert this relationship into an edge and map its properties as attributes in the logical model.
To map relationship properties from a physical edge into the logical model, follow these steps:
-
Open the physical model.
-
Right-click the relationship and click Properties.
The Neo4j Relationship Editor opens.
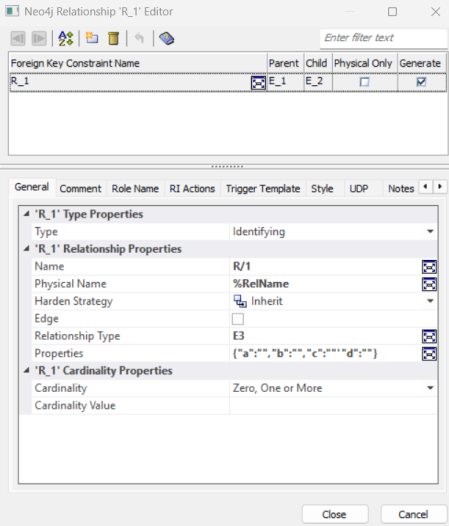
-
Under the Relationship Properties section, set Relationship Type. For example, E3 and add relationship properties (for example, a, b, c, and d) in JSON format.
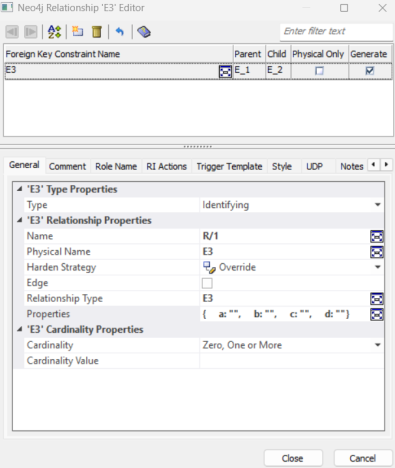
-
Select the Edge checkbox.
-
Click Close.
A logical mediator entity (for example, E3) is created, and the relationship’s properties are added as attributes. For example, a, b, c, and d.
The Edge checkbox is enabled only after defining the Relationship Type.
Converting Intermediate Entities to Edges
In Neo4j models, entities are represented as nodes, and relationships between them are represented as edges. In logical models, an intermediate entity can connect two other entities.
For example, consider a logical model with entities E/6, E/7, and E/8, where E/7 acts as an intermediate entity and contains attributes, a, b, and c.
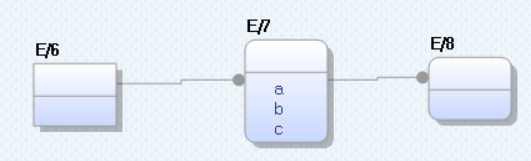
When you view the corresponding physical model, the structure remains the same.
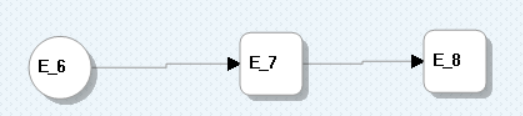
However, you can simplify the physical model by converting the E_7 node into a direct edge between E_6 and E_8 nodes.
Entity to edge conversion is possible only when an entity has both incoming and outgoing relationships.
To convert intermediate entities into edges, follow these steps:
-
Open the physical model.
-
Right-click the intermediate entity (for example, E_7).
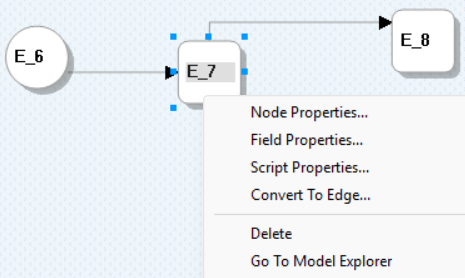
-
Click Convert To Edge.
This creates a direct edge (relationship) between E_6 and E_8.

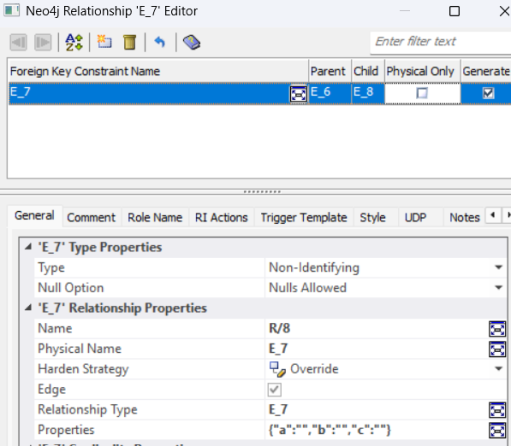
The attributes of the intermediate entity (for example, a, b, and c) are added as relationship properties in JSON format. Also, the Relationship Type property is set to the name of the intermediate entity. To view these properties, right-click the edge, and then click Properties.
The Neo4j Relationship Editor opens and displays the edge's properties.
For more information on how edge mapping works based on operations performed in the physical and logical models, refer to the Managing Mediator Entities, Relationships, Attributes, and Edges section.
Managing Mediator Entities, Relationships, Attributes, and Edges
You can manage mediator entities, relationships, attributes, and edges by performing these actions:
When you add an attribute to a mediator entity in the logical model and convert it, the attribute is automatically added as a relationship property on the corresponding physical edge.
When you rename an attribute in the logical model, the updated name automatically syncs to the corresponding relationship property in the physical model.
When you delete an attribute from the mediator entity in the logical model, the corresponding relationship property is automatically removed from the physical model.
When you change the data type of an attribute in the logical model, the corresponding relationship property in the physical model is updated based on database-specific data type mapping rules.
When you delete a mediator entity in the logical model, its corresponding structure in the physical model is removed, the indirect relationship is deleted, and migrated attributes are cleaned up without creating a direct edge.
When you rename a mediator entity in the logical model, the updated name is reflected in the corresponding relationship details in the physical model.
When you delete a relationship in the logical model, the mediator path is removed, and the corresponding edge and foreign key in the physical model are deleted, disconnecting the affected entities.
When you add a property to a physical edge, a corresponding attribute with the same data type is automatically created in the related logical mediator entity.
When you delete relationships that reference a mediator entity, only the selected relationship is removed each time. The mediator entity remains until no relationships reference it, at which point it is automatically removed from both models.
When you create edges in the physical model, foreign key migration is handled automatically based on the relationship type, introducing mediator entities when needed to keep both models aligned.
Was this helpful?