You can connect to a database using the Reverse Engineering Wizard. The reverse engineering wizard also allows you to select the objects that you want to include in the model and configure model options.
This topic walks you through the steps to connect to a database and reverse engineer a MongoDB model as an example. Similarly, you can connect to any database for scheduling a reverse engineering job based on your requirements. For more information on database specific connection parameter options, refer to Database Connection Parameters topic.
When you click the Reverse Engineer option on the erwin DM Scheduler Event Details page, the Reverse Engineering Wizard appears.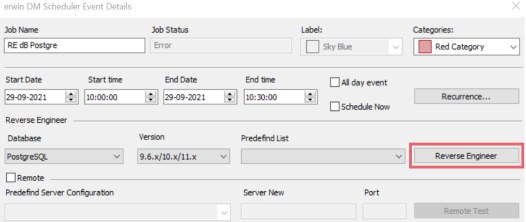
To connect and reverse engineer a model:
-
On the Reverse Engineering Wizard, click Next.
The Connection section appears.
-
On the Connection section, use the available options to connect to the database for reverse engineering models.
You can connect to the database directly or using a connection string. Similarly, for other database types, you can use JDBC, ODBC, or other connection methods based on your requirement.
For more information, refer to the Database Connection Parameters topic.
In the following image, for example, the connection is being established using a connection string.
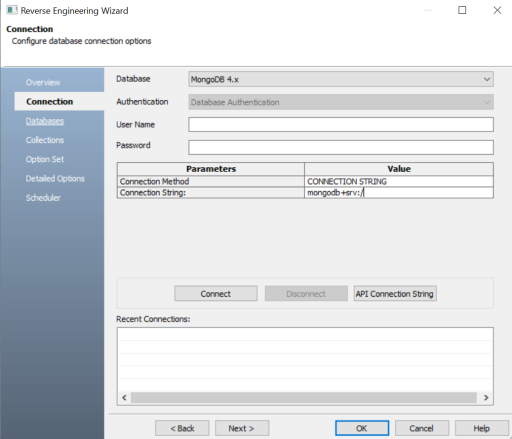
-
Click Connect.
On a successful connection, your connection information is displayed under Recent Connections.
On the Connection tab of the Reverse Engineering Wizard, use the API Connection String button to get the API connection string for your database. For more information, refer to the ISCPersistenceUnit::ReverseEngineer topic in the API Reference.
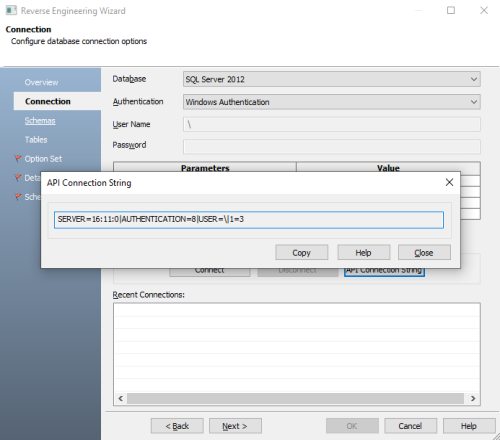
-
Similarly, you can set up other reverse engineering options using this wizard. Click Next to setup other reverse engineering options, or click OK to exit and continue with scheduling a job. The available options differ based on your database. For database-specific reverse engineering options, refer to the Reverse Engineering Options for Databases section.
The Database section appears. It displays a list of available databases. Similarly, for other databases, it displays database specific section for object selection.

-
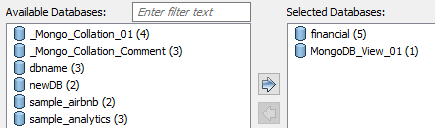
Under Available Databases, select the databases that you want to reverse engineer. Then, click
 .
. 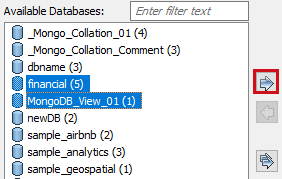
This moves the selected databases under Selected Databases.
-
Click Next.
The Collection section appears. It displays a list of available collections in the databases that you selected in step 8.
Similarly, for other databases, it displays database specific section for object selection.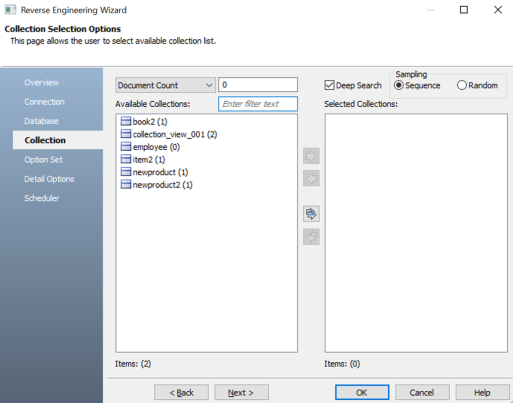
-
Use the following options:
-
Document Count/Document (%): Use this option to specify the number of documents or percentage of total records that the newly generated model schema would contain.
-
Deep Search: Use this option to specify whether the deep search algorithm is used to retrieve the right samples for schema generation.
-
Sampling: Use the Sequence or Random sampling methods to sample records in the selected collections. Sampling enables you to retrieve right estimates for accurate collection schema generation.
-
-
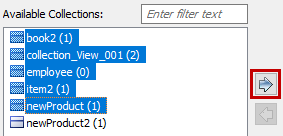
Under Available Collections, select the collections that you want to reverse engineer. Then, click
 .
.
This moves the selected collections under Selected Collections.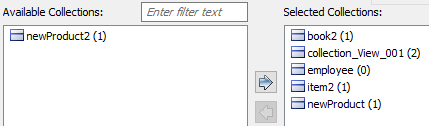
-
Click Next.
The Option Set section appears. It displays the default option set. You can either use the default or a custom option set.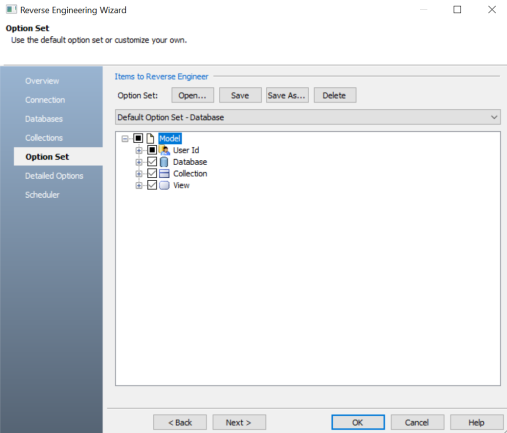
-
Click Next.
The Detail Options section appears. Set up appropriate options based on your requirement.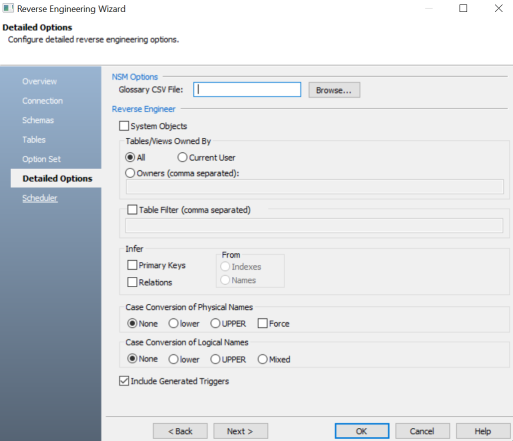
-
Click Next.
The Scheduler section appears.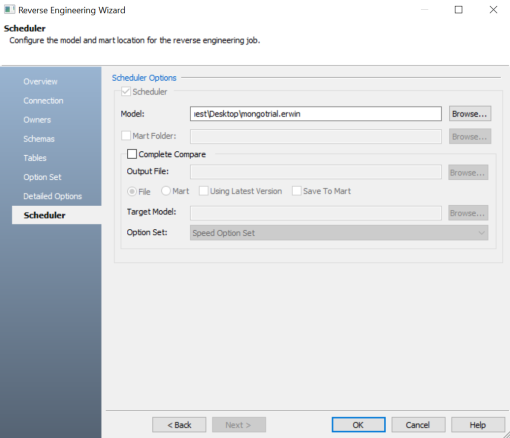
-
On the Scheduler section, configure the scheduler options. For more information, refer the following table:
-
Click OK.
The reverse engineering process starts.

Once the process is complete, based on your selections, a schema is generated and a model is created.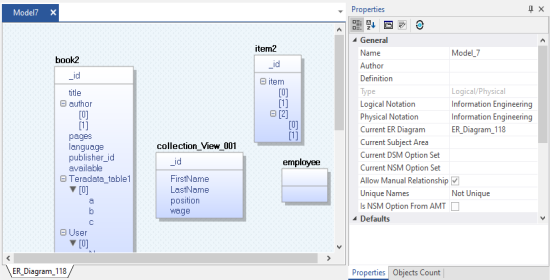
|
Parameter |
Description |
Additional Information |
| Model | Specifies the location and name of the reverse engineered model |
For example: C:\Scheduler\<Model Name>.erwin When you schedule a job on a remote server, ensure the model path is same for remote and local server. |
| Mart Folder | Specifies the location or library in your mart where the reverse engineered model is saved |
To use this option, ensure that you are connected to a mart. For more information, refer to the Connecting to Mart topic. |
| Complete Compare | Specifies whether the Complete Compare (CC) process should run while reverse engineering | |
| Output File | Specifies the location of the CC output file generated | |
| File | Specifies that the target model location is on the local system | |
| Mart | Specifies that the target model location is in the mart | |
| Using Latest Version | Specifies whether the target model is the latest version of the model in the mart | This option is available only when Mart is selected. |
| Save To Mart | Specifies whether the reverse engineered model is saved to the mart | This option is available only when Using Latest Version is selected. |
| Target Model | Specifies the location of the target model for CC | |
| Option Set | Specifies the option set that is used for CC |
Advanced Default Option Set: Indicates that all erwin DM metadata is included. CC works slowest with this option. Speed Option Set: Indicates that only the essential metadata is included. CC works the fastest with this option set. Standard Default Option Set: Indicates that standard metadata is included. CC works fast with this option set compared to the Advanced option set. |
|
Copyright © 2023 Quest Software, Inc. |