erwin Data Intelligence provides support for unstructured data, enabling your organization to ingest, analyze, and govern files that do not follow a predefined schema. This capability extends metadata management to documents and media files, allowing previously unmanaged content to be brought into the erwin DI governance framework.
It supports a wide range of unstructured file formats, including the following:
- Document Formats:
PDF, Word (DOC/DOCX), Excel (XLS/XLSX), Text (TXT), RDF, PPT, HTML, and Markdown. - Media/Binary Formats:
PNG, JPG/JPEG, GIF, BMP, and TIFF.
The extracted information is then transformed into governed metadata assets, represented as tables, columns, and attributes within the catalog. Additionally, Sensitive Data Identification (SDI) is applied automatically to detect and tag sensitive information.
Files up to 1 GB can be processed directly through the UI, while larger files can be best handled using Scheduled Scans to minimize performance impact.
Once published, the metadata is available for search, governance, and analysis.
Prerequisite
Before profiling unstructured data, you must install and configure Tesseract. Tesseract OCR is required on Windows, Red Hat and Ubuntu servers to process image-based files.
Installing and Configuring Tesseract
This section walks you through the steps to install and configure Tesseract for Windows, Red Hat and Ubuntu. This process involves:
To install and configure Tesseract installer, follow these steps:
-
Visit the https://github.com/UB-Mannheim/tesseract/wiki page, and download the Windows 64-bit Tesseract installer.
-
Run the installer and complete the installation using default settings.
-
Click the Windows Start icon.
-
In the search bar, type Edit the system environment variables and press Enter.
-
Click Environment Variables.
The Environment Variables window opens.
-
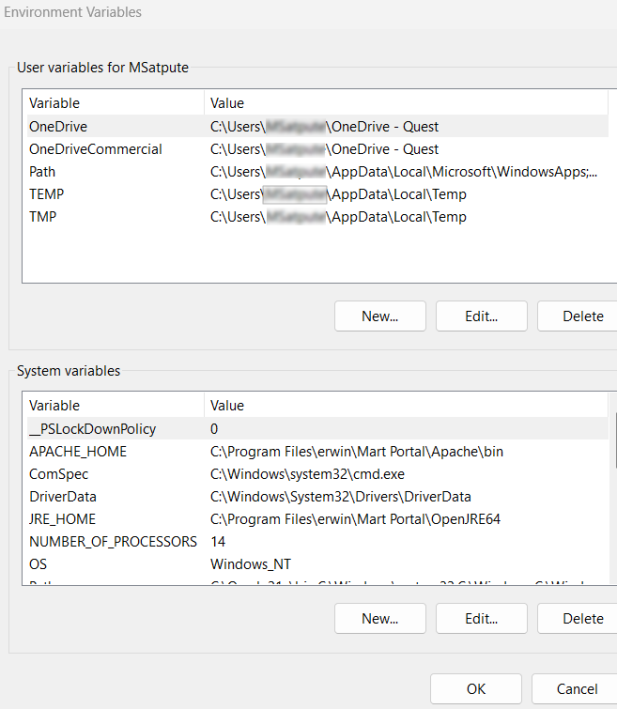
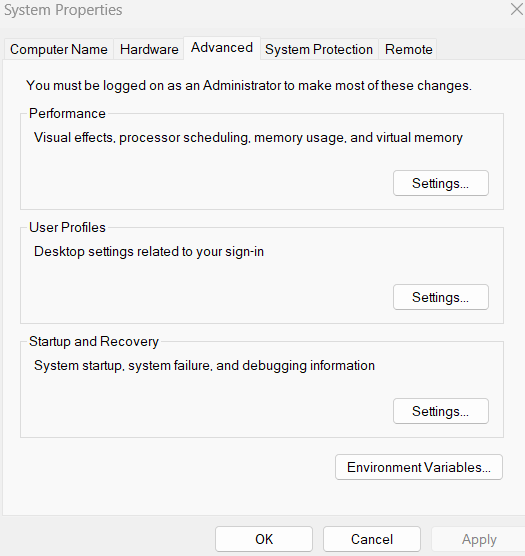
Under System variables, click New.
-
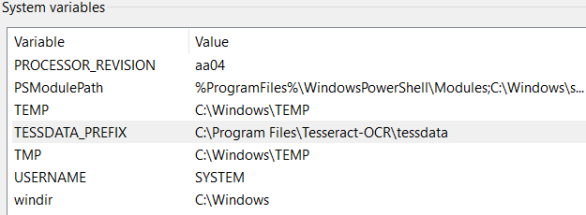
In the Variable name field, enter TESSDATA_PREFIX.
-
In the Variable value field, enter C:\Program Files\Tesseract-OCR\tessdata.
-
Click Ok.
The variable and its value are added under System variables section.
-
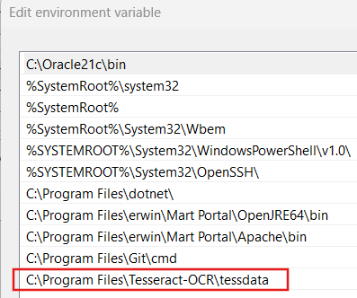
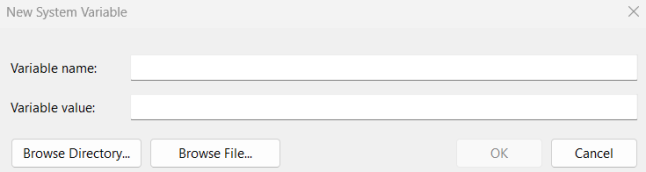
Under System variables, search for Path and then double-click on it.
-
Click New and enter C:\Program Files\Tesseract-OCR\tessdata.
The environment variable is added.
-
Click Ok.
-
On the Environment Variables window, click Ok.
-
Restart the Tomcat service.
The System Properties window opens, and the Advanced tab opens by default .
The New System Variable window opens.
The Edit environment variable window opens.
Open a terminal window and run the following commands:
-
Enable EPEL Repository
sudo dnf install -y https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm
-
Install Tesseract 4
sudo dnf install -y tesseract
-
Install English language data
sudo dnf install -y tesseract-langpack-eng
-
Verify installation
tesseract --version
The environment variable is set.
Tesseract 4 supports only for RHEL 8.5.
-
Restart the Tomcat service.
Open a terminal window and run the following commands:
-
Install Tesseract 4
sudo apt install tesseract-ocr
-
Install Tesseract libraries
sudo apt install libtesseract-dev
-
Install English language data
sudo apt install tesseract-ocr-eng
-
Verify installation
tesseract --version
The environment variable is set.
-
Restart the Tomcat service.
Profiling Unstructured Data
To profile unstructured data for automated ingestion, follow these steps:
- Click New Environment.
- Select Other.
- Switch to the Connection Properties tab.
- Enter appropriate values in the fields. Refer to the following table for field descriptions.
Field Name
Description
Driver Name
Specifies the JDBC driver name for connecting to the database. Set this field to com.quest.erwin.jdbc.OpenJDBCDriver.
Url
Specifies the full JDBC URL that represents the location from which unstructured data files are read. All files located within this path and its subfolders are considered for scanning.
This field requires a network drive path that the Tomcat service has access to.
Set this field to jdbc:openjdbc:<path accessible to Tomcat>.
For example, jdbc:openjdbc:C:\XYZ.
IP Address/Host Name Specifies the IP address or server host name of the database.
Set these fields to NA.
DBMS Name/DSN Specifies the database name being used to connect to the environment.
Set this field to NA.
Port Specifies the port to connect with the database.
Set this field to NA.
User Name Specifies the database user name.
Set this field to NA.
- Click
 to save connection.
to save connection.
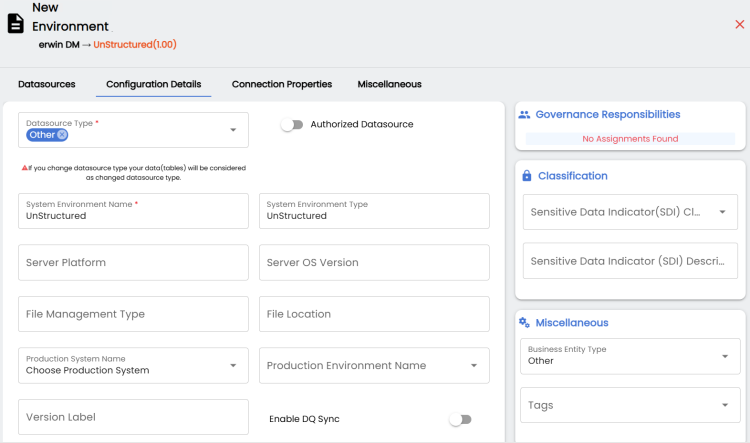
The New Environment page appears and displays supported database in the Datasources tab.

The Configuration Details tab appears and displays connection details for Other datasources. The connection details vary based on database selection.
Alternatively, enter a keyword in the search bar to search for datasources.
Enter appropriate values in the fields. Fields marked with a red asterisk are mandatory.
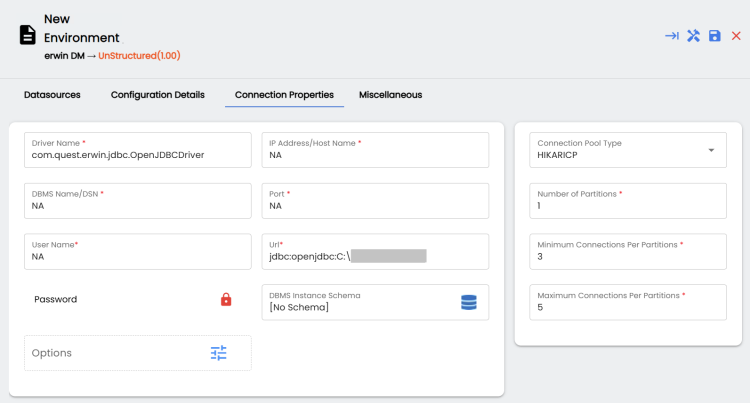
This allows erwin DI to ingest and scan all the files.
|
Copyright © 2026 Quest Software Inc. |